What to Look for in a Quality Sheet Metal Forming Machine
Understanding Sheet Metal Forming Machines
Definition of a Sheet Metal Forming Machine
A Sheet Metal Forming machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to transform flat sheets of metal into specific shapes and configurations. Utilizing processes such as bending, cutting, stamping, and rolling, these machines can produce intricate designs essential for various industrial applications. By employing precise mechanical actions and leveraging computer numerical control (CNC) technologies, modern sheet metal forming machines ensure accuracy and consistency in production.
Importance in Various Industries
Sheet metal forming machines play a pivotal role across multiple industries. Their versatility and efficiency make them indispensable in sectors ranging from automotive to construction.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, sheet metal forming machines are utilized to manufacture a wide array of components, including body panels, chassis, and structural parts. The high degree of precision afforded by these machines ensures that each component meets stringent quality standards, contributing to the overall safety and performance of the vehicle.
Quality is of utmost importance to XINBO. Each machine undergoes three rounds of inspection before being shipped to customers. This rigorous quality inspection process guarantees that the machines meet the highest standards and are free from any defects or issues.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands materials that are both lightweight and robust. Sheet metal forming machines are critical in producing components such as fuselages, wing structures, and brackets. The ability to work with various metals, including aluminum and titanium, makes these machines essential for aerospace applications where precision and material performance are paramount.
Construction and HVAC Industry
In the construction sector, sheet metal forming machines are employed to create essential building components like beams, columns, and roofing materials. Additionally, the HVAC industry relies on these machines to produce ductwork, vents, and other airflow management components. The efficiency and accuracy provided by these machines ensure that the produced parts meet the necessary dimensional and quality requirements.
Key Features of a Quality Sheet Metal Forming Machine
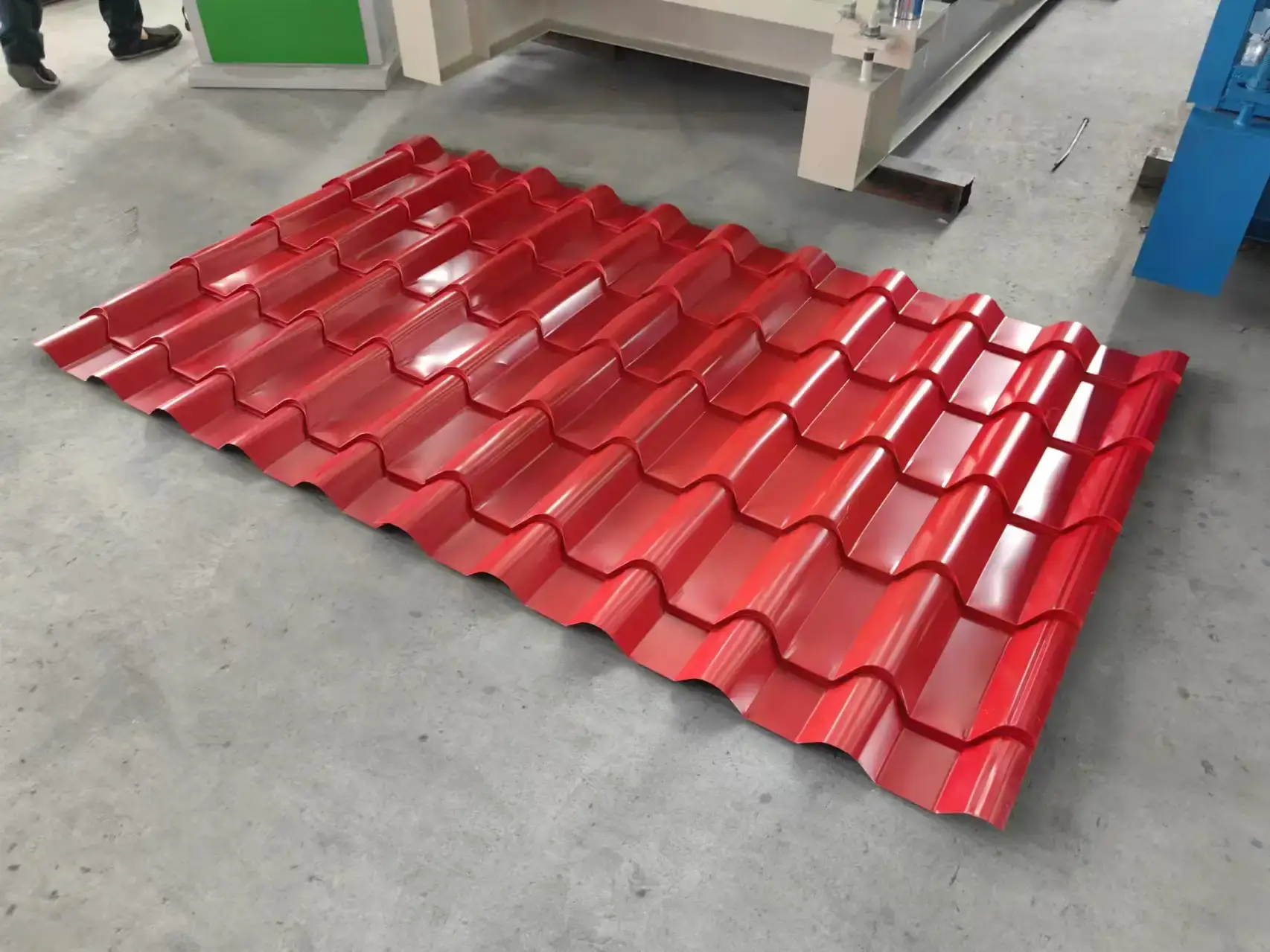

Material Compatibility
One of the foremost considerations in selecting a sheet metal forming machine is its material compatibility. A high-quality machine should support a diverse array of metals and provide flexibility in terms of thickness and type.
Variety of Metals Supported
A robust sheet metal forming machine should be capable of handling different metals such as aluminum, steel, copper, and titanium. This versatility allows industries to use a single machine for various applications, reducing the need for multiple specialized equipment and thus cutting down on costs and space requirements.
Thickness Range
A machine that supports a broad thickness range is advantageous as it offers more flexibility in production processes. Whether working on thin sheets for lightweight components or thick plates for structural elements, the machine should maintain its precision and efficiency across different material thicknesses.
Precision and Accuracy
Precision and accuracy are critical attributes for any sheet metal forming machine. The machine must deliver consistent results with minimal tolerances to ensure that each part meets the required specifications. This level of precision is achieved through advanced CNC systems, which allow for meticulous control over the forming processes.
Production Speed and Efficiency
A key feature of a quality machine is its ability to deliver high production speeds without sacrificing accuracy. Efficient production speed enables manufacturers to meet high demand and reduce lead times, making their operations more competitive in the marketplace. Additionally, machines equipped with automation capabilities can further enhance productivity by minimizing manual intervention and reducing cycle times.
Software Integration and Automation Capabilities
The integration of sophisticated software and automation technologies is essential for modern sheet metal forming machines. CAD/CAM software facilitates the design and simulation of parts before actual production, ensuring optimal use of materials and reducing errors. Automation capabilities, including robotic loading and unloading systems, further streamline the manufacturing process, increasing throughput and reducing labor costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Machine
Size and Capacity Requirements
When selecting a sheet metal forming machine, it is vital to consider the size and capacity requirements specific to your production needs. Machines come in various sizes and capacities, and choosing one that aligns with your production volume and the dimensions of the parts you intend to produce is crucial. Understanding these factors ensures that the machine can handle the workload efficiently without unnecessary wear and tear.
Ease of Maintenance and Durability
Ease of maintenance and durability are key factors that contribute to the long-term operational efficiency of a sheet metal forming machine. Regular maintenance is necessary for keeping the machine in optimal working condition, and machines designed with easy access to critical components can simplify this process. Additionally, robust construction and high-quality materials enhance durability, reducing the frequency of breakdowns and extending the machine’s lifespan.
Safety Features
Safety is a paramount concern in any industrial environment, and sheet metal forming machines must incorporate comprehensive safety features. These may include emergency stop buttons, safety guards, and automated shut-off systems in case of malfunction. Ensuring that the machine complies with international safety standards protects operators and minimizes the risk of accidents, fostering a safer workplace.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Energy consumption is an important consideration, as it directly impacts operational costs. Modern sheet metal forming machines are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing power usage during operation. Additionally, considering the environmental impact of the machine is essential for sustainable manufacturing practices. Machines that minimize waste and support recycling initiatives can contribute to your company’s environmental goals.
Types of Sheet Metal Forming Machines
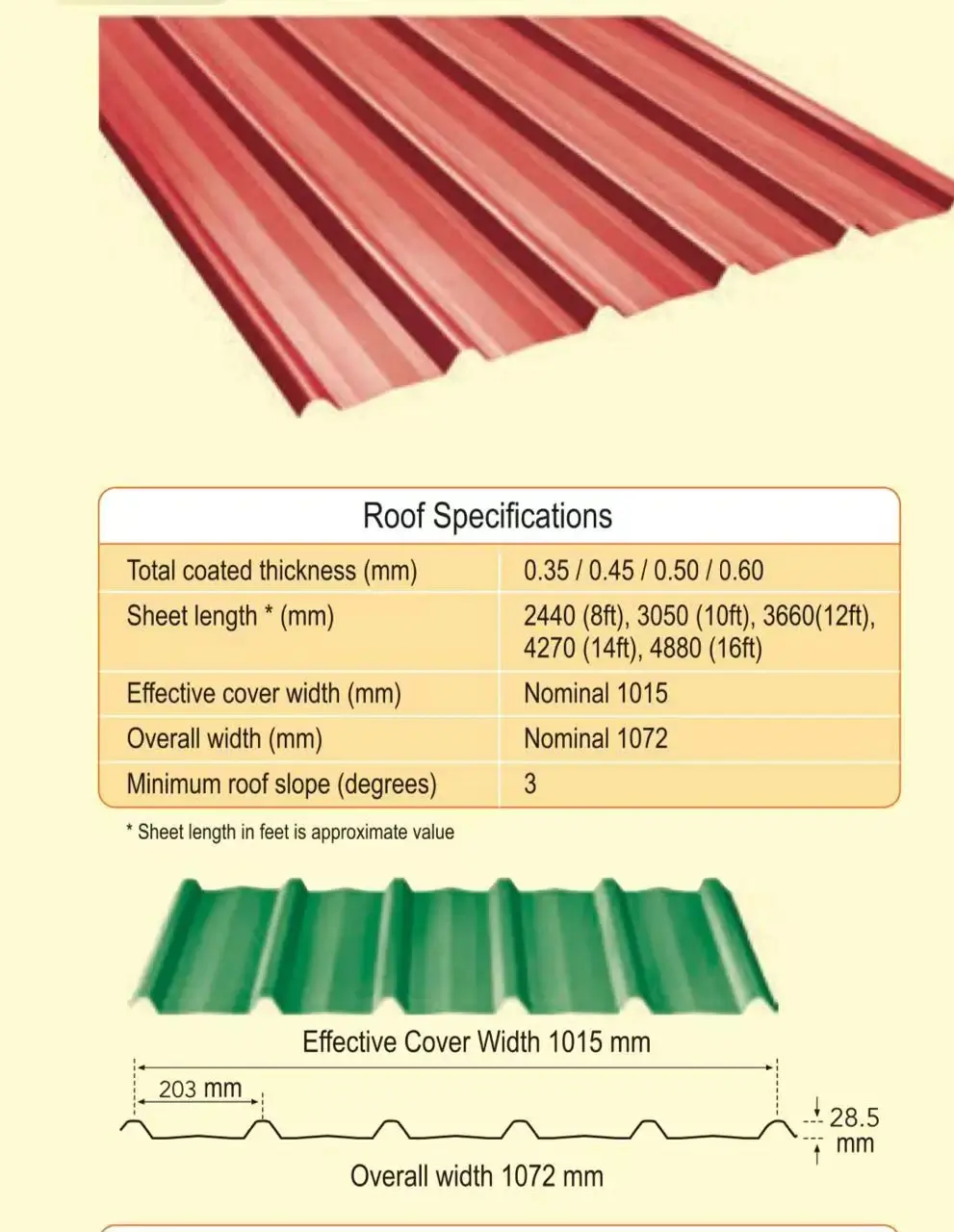
Press Brakes
Press brakes are essential for bending and shaping metal sheets. They are available in several types, each offering distinct advantages.
Hydraulic Press Brakes
Hydraulic press brakes utilize hydraulic fluid to exert force on the metal sheet. They provide consistent pressure and are ideal for handling thick materials. Their ability to operate at various speeds makes them versatile for different production needs.
Mechanical Press Brakes
Mechanical press brakes rely on mechanical components and flywheels to deliver force. They are typically faster than hydraulic versions, making them suitable for high-speed operations. However, they may not provide the same level of control and precision as hydraulic press brakes.
Electric Press Brakes
Electric press brakes use electric motors to generate force. They offer superior control and precision, making them ideal for intricate and delicate work. Additionally, they are energy efficient and require less maintenance compared to hydraulic and mechanical counterparts.
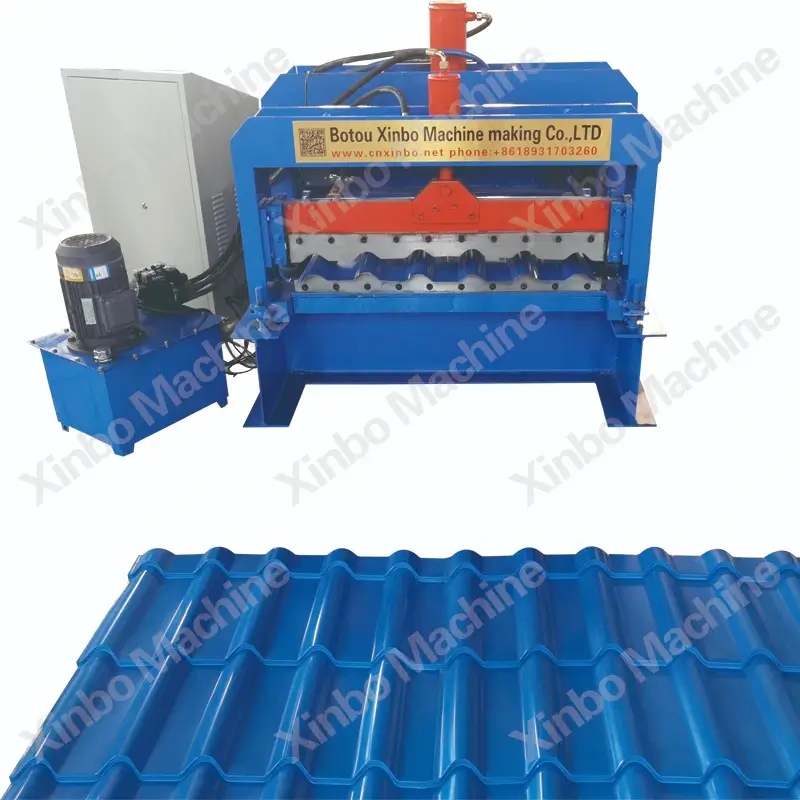
Roll Forming Machines
Roll forming machines are used for continuous bending of long strips of metal into desired cross-sectional shapes.
Single Stand Roll Formers
Single stand roll formers consist of a single set of rolls that shape the metal sheet in one pass. They are suitable for producing smaller quantities and simpler shapes, making them cost-effective for low-volume applications.
Multi-Stand Roll Formers
Multi-stand roll formers have multiple sets of rolls, allowing for more complex shapes and higher production volumes. They provide tighter tolerances and consistent quality, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing operations.
Stamping Presses
Stamping presses are used for cutting and shaping metal by deforming it with a die.
Mechanical Stamping Presses
Mechanical stamping presses use mechanical movements to drive the die into the metal sheet. They are known for their speed and are suitable for high-volume production runs.
Hydraulic Stamping Presses
Hydraulic stamping presses utilize hydraulic systems to apply force. They offer greater control and are capable of handling thicker materials. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high precision and varied force application.
Common Applications of Sheet Metal Forming Machines

Fabrication of Automotive Parts
Sheet metal forming machines are extensively used in the automotive industry for fabricating various parts such as body panels, chassis, and structural components. Their ability to produce high-precision parts ensures that all components fit perfectly, contributing to the vehicle’s overall performance and safety.
Production of Household Appliances
Household appliances, such as refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines, incorporate many sheet metal components. Forming machines are employed to create these parts with precision, ensuring the functionality and aesthetics of the final products.
Creation of HVAC Ductwork
HVAC ductwork requires precise and efficient production to ensure proper airflow and energy efficiency. Sheet metal forming machines are used to create ducts, vents, and other components, meeting the strict dimensional and performance specifications needed for HVAC systems.
Cost Implications
Initial Investment
The initial investment in a sheet metal forming machine can be substantial. However, the cost must be weighed against the machine’s capabilities, lifespan, and the efficiencies it offers. Investing in a high-quality machine can lead to long-term savings through reduced maintenance and operational costs.
Operational Costs over Time
Operational costs include energy consumption, maintenance, and labor expenses. Machines that are energy-efficient, easy to maintain, and capable of automation can significantly reduce these costs over time, making them a more economical choice in the long run.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the return on investment involves considering the machine’s initial cost, operational savings, and the value added by increased production capabilities. A well-chosen machine can offer a high ROI by enhancing productivity, reducing wastage, and improving the overall quality of the produced parts.
Future Trends in Sheet Metal Forming Technology
Advances in Automation and Robotics
The integration of advanced automation and robotics is transforming sheet metal forming. Robots are increasingly used for loading and unloading, while automated systems control the forming process with high precision. These advancements lead to higher production speeds, reduced labor costs, and improved safety.
Enhanced Integration with Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing involves the integration of IoT devices, data analytics, and advanced software to optimize production processes. In sheet metal forming, smart manufacturing can enhance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time quality control, leading to more efficient and adaptive production environments.
Making the Right Purchase Decision
Choosing the right sheet metal forming machine involves careful consideration of various factors including material compatibility, precision, production speed, and cost implications. By thoroughly evaluating your specific needs and the features of available machines, you can make an informed decision that will optimize production capabilities and ensure a high return on investment.
XINBO is a company that prides itself on providing excellent custom services to its customers. With a team of professional engineers and designers, XINBO is able to quickly and accurately design detailed drawings according to the specific needs and requirements of its customers. This ensures that the final product matches the desired profile and specifications.
Related Posts

Good quality
XinBo machine making CO. LTD is a professional manufacturer and exporter in roll forming machine,
VIEW MORE→

 Spanish
Spanish Russia
Russia