Roll Forming vs. Extrusion: Understanding the Key Differences in Metal Manufacturing
Introduction to Metal Manufacturing Methods
In the realm of industrial production, metal fabrication plays a pivotal role, accounting for more than 50% of the products and amenities used in daily life. The global metal forming market for automotive alone was valued at a staggering USD 172.5 billion in 2020, with projections to reach USD 202.2 billion by 2025. This growth is attributed to factors such as increasing vehicle production and the trend towards lightweight vehicles.
When it comes to shaping metal, manufacturers have a variety of methods at their disposal. These methods are crucial in transforming raw materials into the desired shapes and structures required for different applications. Among the common methods used in the industry are roll forming and extrusion, each offering distinct advantages and applications based on specific manufacturing needs.
Choosing the right method for metal shaping is of paramount importance as it directly impacts both the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing process. The selected method also has significant cost considerations that can influence overall project budgets and profitability.
The research methodology employed in analyzing these methods involves various secondary sources, paid databases, and directories such as Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA), Factiva, Bloomberg, Hoovers, among others. This ensures that the information presented is well-researched and reliable.

Exploring Roll Forming and Its Advantages
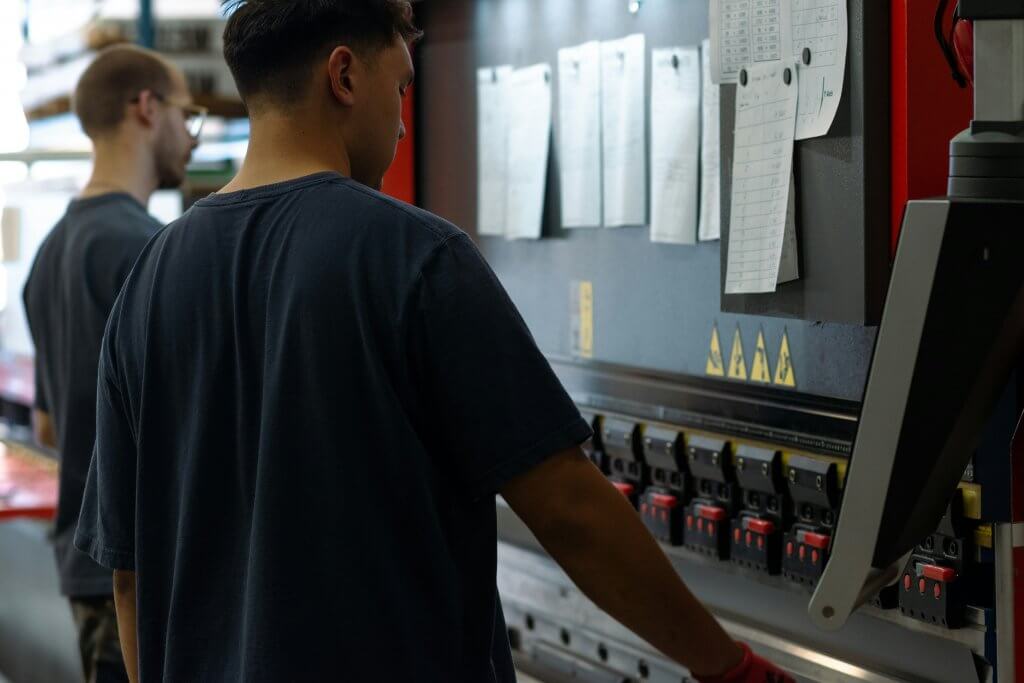
Roll forming is a metal shaping process that involves passing a long strip of metal through consecutive sets of rolls, gradually bending the metal into the desired cross-sectional shape. This method is widely used in various industries for producing continuous profiles with consistent cross-sections, making it an efficient and cost-effective manufacturing technique.
What is Roll Forming?
The Process Explained
The roll forming process begins with a coil of metal, which is fed into the first set of rolls. Each set of rolls performs a specific bending or forming operation on the metal as it progresses through the machine. The final shape is achieved through a series of gradual deformations, resulting in a uniform and precise profile along the entire length of the material.
Types of Metals Suitable for Roll Forming
Roll forming can be applied to a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, and alloys such as stainless steel. Its versatility in working with different materials makes it an attractive option for manufacturers across various industries.
Benefits of Using a Roll Forming Machine
Efficiency and Consistency
A key advantage of utilizing a roll forming machine is its high level of efficiency. The continuous nature of the process allows for rapid production rates, minimizing material waste and reducing labor costs. Additionally, the consistency achieved in shaping the metal ensures uniformity in the final products, meeting quality standards without variation.
Versatility in Metal Shapes and Sizes
Roll forming machines offer unparalleled flexibility in creating an extensive range of profiles, from simple angles and channels to complex geometries. This adaptability makes roll forming suitable for diverse applications across construction, automotive, aerospace, and other sectors where unique shapes are required.
The invention related to roll-forming machines emphasizes their novel features that contribute to improved manufacturing processes. These advancements align with the benefits highlighted above, showcasing how modern technologies continue to enhance roll forming capabilities.
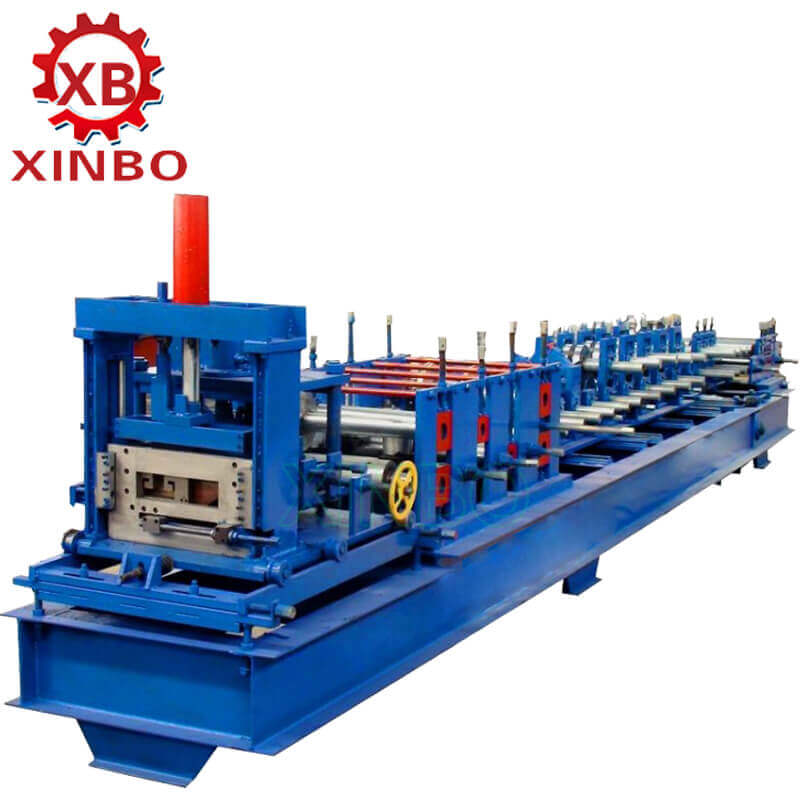
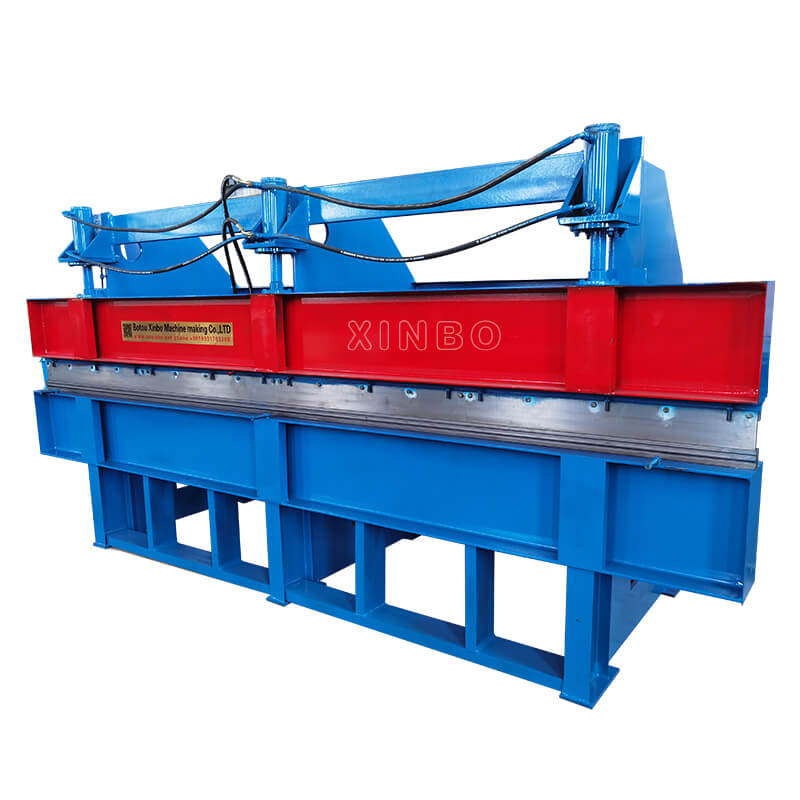
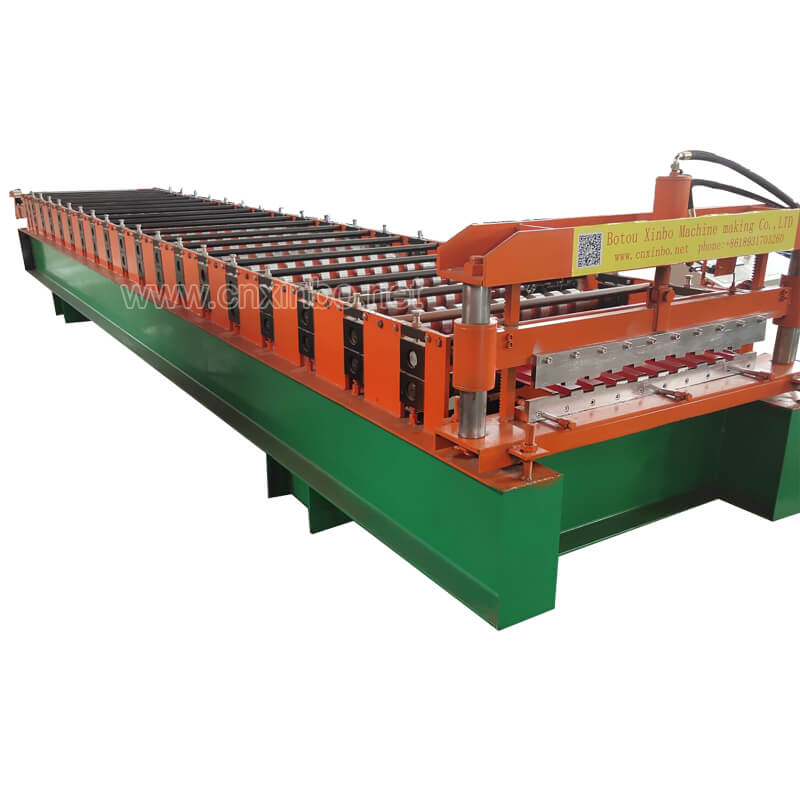
Xinbo Machine Making Co. Ltd, established in China since 2014, is a manufacturer specializing in roll forming machines. These machines are designed with new and innovative technology to meet the needs of customers in Europe, UK, Canada, and beyond.
Xinbo offers various types of roll forming machines, including U channel rolling forming machines, purlin roll forming machines, and floor deck roll forming machines. The U channel rolling forming machine can roll metal sheets into U-shaped channels of different sizes and thicknesses. The purlin roll forming machines are used to produce purlins, the horizontal beams that support the roof of a building, in various sizes and shapes. The floor deck roll forming machine is designed to produce different types of floor decking panels, including corrugated sheets and trapezoidal sheets.
Understanding Extrusion in Metal Manufacturing
In the realm of metal manufacturing, extrusion stands as a versatile and widely utilized process for shaping metals into desired profiles. This section delves into the fundamental aspects of extrusion, shedding light on its operational mechanisms and the materials compatible with this innovative method.
The Extrusion Process Overview
How Extrusion Works
The extrusion process involves forcing a metal billet or ingot through a shaped die to produce a continuous profile. This is achieved by applying compressive force using either a mechanical or hydraulic press. As the metal is forced through the die, it undergoes plastic deformation, resulting in an elongated shape that mirrors the contours of the die. The ability to create complex cross-sectional profiles makes extrusion suitable for a wide array of applications across industries.
Materials Compatible with Extrusion
Extrusion is compatible with various metals and alloys, offering manufacturers flexibility in material selection based on specific project requirements. Common materials suitable for extrusion include aluminum, copper, brass, and various steel alloys. These materials exhibit favorable characteristics during the extrusion process, such as malleability and ductility, allowing for seamless shaping into intricate designs.
The versatility of extruded metals extends to their application in architectural frameworks, automotive components, electrical conduits, and consumer goods. This adaptability underscores the significance of extrusion as a preferred method for achieving precise and intricate profiles essential for diverse industrial applications.
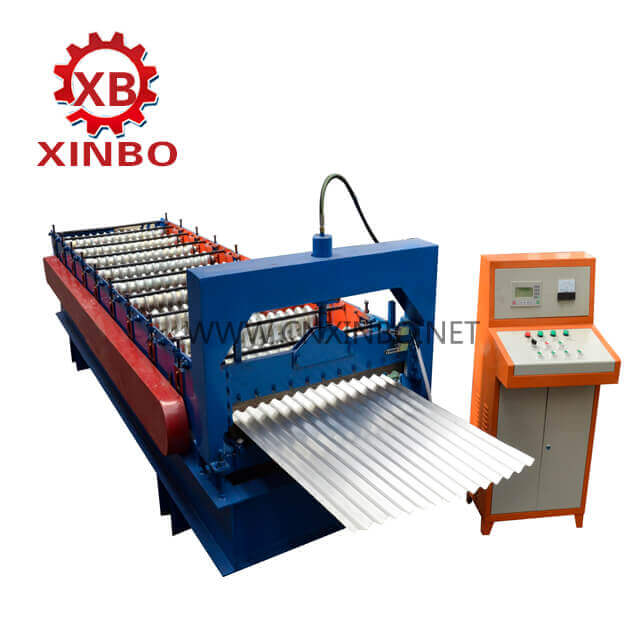

Roll Forming Machine vs. Extrusion Press: Key Differences
Comparing the Machinery Used in Roll Forming and Extrusion
When comparing roll forming and extrusion, it’s essential to understand the distinct machinery used in each process. Roll forming involves an intricate die and several passes of the material to form the desired shape, while extruded aluminum process involves a single piece of metal that is simple to fabricate and thus less costly than a roll formed die.
In roll forming, a roll forming machine utilizes a series of rolls to gradually bend the metal into the desired cross-sectional shape. This method allows for more in-line fabrication, medium to large runs, and higher volume orders. On the other hand, extrusion employs a hydraulic press to force a metal billet or ingot through a shaped die, allowing for multiple cross-sections, wall thickness control, and incredibly low tooling costs.
Design and Operational Differences
The design and operational variances between roll forming machines and extrusion presses are significant factors that influence their suitability for different manufacturing needs. Roll forming is a faster process that uses less material, making it more cost-efficient for very large projects. However, the roll-forming dies and setup are more complex, intricate, and thus more expensive compared to the extruded aluminum process.
Roll forming tooling is more extensive than extrusion and can therefore cost more. Still, these costs can be offset by the ease of adding features along the length of the roll-formed section when compared to achieving the same result with an aluminum extrusion.
Suitability for Different Manufacturing Needs
Volume plays a crucial role in determining which method is best suited for specific manufacturing needs. If the run volume is low, extrusion tooling costs will most likely be less than roll forming. However, if the run volume is high, per piece setup and labor costs should favor roll forming.
Final Thoughts on Choosing Between Roll Forming and Extrusion
Recap of Key Points
After delving into the intricacies of roll forming and extrusion, it becomes evident that both methods offer unique advantages and applications in metal manufacturing. The decision to choose between roll forming and extrusion hinges on various factors, including the specific requirements of the project, volume considerations, and material compatibility.
Ethical Manufacturing Influence: Ethical manufacturing focuses on sustainability, efficiency, and the well-being of all involved in the manufacturing process. It influences a company’s approach toward environmental degradation caused by its operations. This holistic approach maintains sustainable standards and has a positive impact on communities. It also leads to improved productivity, attracts customers, and has clear financial benefits.
When considering roll forming, its efficiency in producing continuous profiles with consistent cross-sections makes it an attractive option for medium to large production runs. The versatility offered by roll forming machines allows for the creation of complex geometries essential for diverse industrial applications.
On the other hand, extrusion stands as a versatile process suitable for shaping metals into intricate profiles essential for architectural frameworks, automotive components, electrical conduits, and consumer goods. Its ability to create complex cross-sectional profiles using materials like aluminum, copper, brass, and steel alloys underscores its significance in various industries.
The decision-making process should include a thorough evaluation of cost-efficiency based on volume considerations. While roll forming may be more cost-efficient for large projects due to its rapid production rates and minimal material waste, extrusion offers lower tooling costs suitable for smaller production runs.
In conclusion, manufacturers must carefully assess their project requirements while considering ethical manufacturing principles to make an informed choice between roll forming and extrusion. By aligning with sustainable standards and prioritizing the well-being of all involved stakeholders, companies can achieve optimal results while contributing positively to their communities.
By embracing ethical manufacturing practices throughout the decision-making process, manufacturers can uphold sustainable standards while delivering high-quality products tailored to meet diverse industrial needs.
Related Posts

Good quality
XinBo machine making CO. LTD is a professional manufacturer and exporter in roll forming machine,
VIEW MORE→

 Spanish
Spanish Russia
Russia